This year, with the popularization of the RWA concept and the growth of the stablecoin market, the number of related projects has increased rapidly.
Last week, the stablecoin protocol USD.AI completed a $13 million Series A funding round in the primary market. By introducing GPU property rights, the project connects Decentralized Token Offering (DePIN), AI, Reliable Token Offering (RWA), and stablecoins. This initiative can be considered a form of "Infra-Fi," potentially offering new insights into DePIN.
USD.AI is positioned as a decentralized credit protocol: emerging AI companies can use their GPU hardware as collateral to obtain loans. USD.AI has created the CALIBER standard, which represents GPU ownership through on-chain NFTs and incorporates insurance, valuation, and redemption mechanisms.
USD.AI created the CALIBER standard, which represents GPU ownership in the form of on-chain NFTs and binds insurance, evaluation, and redemption mechanisms on the chain.
This means that GPU ownership, collateralization, and redemption can all be executed on-chain. USD.AI's business model reveals that as a stablecoin project with revenue, its revenue comes from AI hardware and US Treasury bonds. GPU hardware generates revenue through methods such as computing power leasing, and the interest on the loan is then distributed to sUSDAI stablecoin holders.
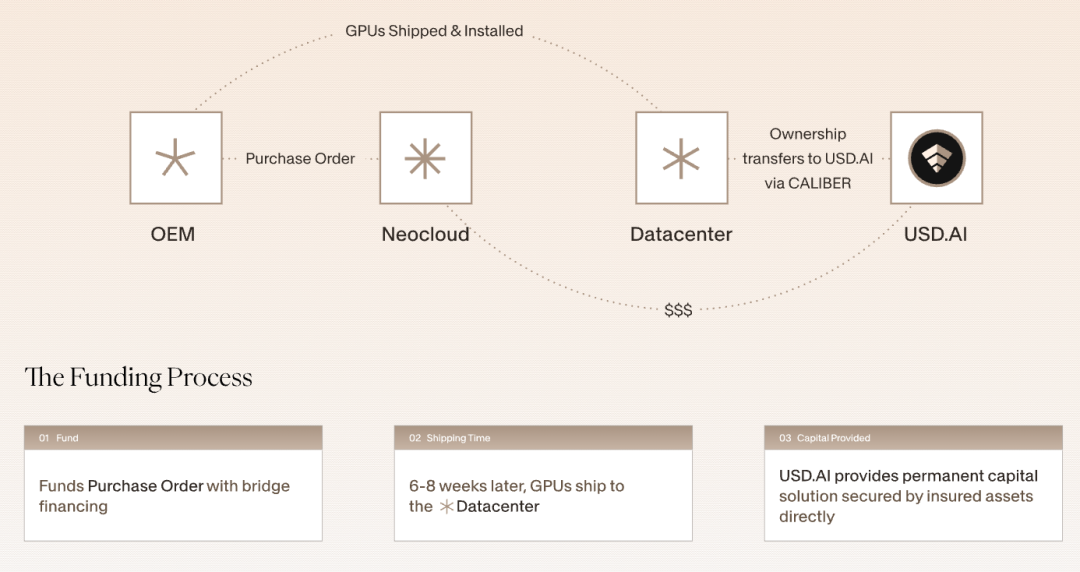
In this model, GPUs aren't just hardware and computing power; they generate cash flow through AI training and inference services, thus supporting the value of the collateral. If no one borrows money for the time being, the idle funds will be invested in U.S. Treasuries to earn a return.
The protocol designs a dual-token model:
USDai: Anchored to the US dollar, it serves as a settlement tool for loan issuance and liquidation.
sUSDai: A yield-generating stablecoin whose value is supported by the revenue generated by GPUs (such as AI training rental income) and distributes the revenue to investors.
Based on this, the official target APR of 15% to 25% was set (the current APR is 6.76%, with an expected 7.83%, and a TVL of nearly $50 million during the beta period). This decentralized credit model for AI startups, secured by calculable and liquid computing power assets, aligns well with collateralization logic and risk models. However, achieving this interest rate through low-liquidity property rights raises questions and challenges due to the black-box nature and decentralized transparency of RWAs.
Regardless, financializing GPU ownership and transforming physical property into programmable financial assets also provides new insights into DePIN+DeFi. Within the DePIN space and Infra-Fi concepts, we can see the following trends:
1. Machine Collateralization, Computing Power Assetization, and Infra-Fi
In the on-chain market, hardware infrastructure like GPUs can be used as productive assets, transforming from hardware resources into a new asset class capable of collateralization and lending. In the future, the business scope of DePIN and RWA may no longer be limited to the strict legal and compliance constraints of off-chain areas. DePIN and AI-related infrastructure, as well as the more enterprise-grade hardware devices behind them, may enter the market.
2. DePIN + RWA
The off-chain assets involved in DePIN typically have practical applications and business revenue. The key focus of the DePIN project is how to transfer the profitability of off-chain assets to the on-chain DeFi revenue pool. In this case, machinery and equipment serve as both on-chain collateral and RWA assets, indirectly entering the DeFi market cycle.
3. Integration/Acceleration of AI and Crypto
This innovation will make the financing costs of AI companies more market-oriented: for small AI teams, obtaining loans by mortgaging GPUs further lowers the threshold, but also places higher requirements on interest returns; for stablecoin holders, even if they do not understand the AI market, they can indirectly participate in investments similar to "AI corporate bonds" to obtain returns and potential incentives.
4. Parallel narrative
In the same cycle, market sentiment will switch between different tracks, most likely different aspects of the same logic. We can further pay attention to the combination and progress of BTCFi with RWA, DePIN and other directions.
The core logic of the original DePIN flywheel is "resource sharing," where users become resource providers, driving development through "resource sharing + user incentives." GPU property lending, on the other hand, unlocks liquidity through the financialization of hardware. Enterprises generate capital flows through financing and computing power monetization, forming a new flywheel.
Driven by cash flow repatriation, this new model creates synergy between decentralized capital markets and the AI industry's production capacity (e.g., GPU clusters and AI model training), shifting from "shared resources" to assetization and financialization. Hardware resources can not only generate cash flow through rentals but also serve as on-chain collateral, accelerating credit expansion and capital market circulation.
If successful, this could open up a financial market for "machine collateralization," transforming Infra into a financially viable "machine version" of RWA through on-chain protocols and entering the DeFi market. The range of assets could also broadly include data storage, computing, bandwidth, electricity, and more, driving the "mobility" of DePIN in a new cycle.








