By Lacie Zhang, Researcher at Bitget Wallet
Introduction: Asset Anxiety in the Low-Interest Rate Era
On September 17th, Eastern Time, Federal Reserve Chairman Powell announced a 25 basis point reduction in the target range for the federal funds rate to 4.00% to 4.25%. This decision not only confirmed the expectations for a rate cut that had been building since the end of last year, but also reinforced the market consensus that the path for rate cuts will remain open: the market generally predicts that there is room for two more rate cuts totaling 50 basis points this year.
Each Federal Reserve interest rate decision is based on a comprehensive assessment of the U.S. job market and economic growth prospects, with its impact rippling through global capital markets. The start of this round of rate cuts officially heralds the entry of global investment into a "low-interest era." Whether it's bank savings, government bonds, or money market funds, the yield ceilings on traditional, stable investments are being pushed lower and lower, fueling growing investor anxiety over an "asset shortage."
While traditional finance's yield curve continues to decline, Web3 stablecoin investment products have captured public attention with their exceptionally high yields. These USD-backed stablecoin investment products, whether within decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols or on centralized digital asset platforms, frequently offer annualized returns of 5% or even as high as 20%. This raises questions: Where does the interest on assets strictly pegged to the US dollar come from? Are these astonishingly high returns a fleeting market bubble or the emergence of a disruptive financial model? In this article, the Bitget Wallet Research Institute will analyze these phenomena, uncovering the underlying logic behind these high returns and objectively assessing the opportunities and potential risks of this "new game."
1. “Current Savings” in the Digital World: Three Mainstream Models of Stablecoin Financial Management
Before exploring mainstream models, it's important to first clarify the definition of "stablecoin investment." Simply put, "stablecoin investment" is a digital equivalent of a "bank deposit." Investors deposit their stablecoins (such as USDC and USDT), which are pegged 1:1 to the US dollar, into a specific platform or protocol to earn interest. The core goal is to provide holders with a relatively substantial and predictable annualized return through on-chain or platform-based yield strategies, while maintaining the stability of the principal. This typically maintains the high liquidity of demand deposits.
Currently, stablecoin financial products on the market can be divided into three main modes based on their underlying operating logic and asset custody methods: DeFi native mode, CeFi custody mode, and a hybrid mode that combines DeFi and CeFi.
Comparison table of mainstream stablecoin financial management models
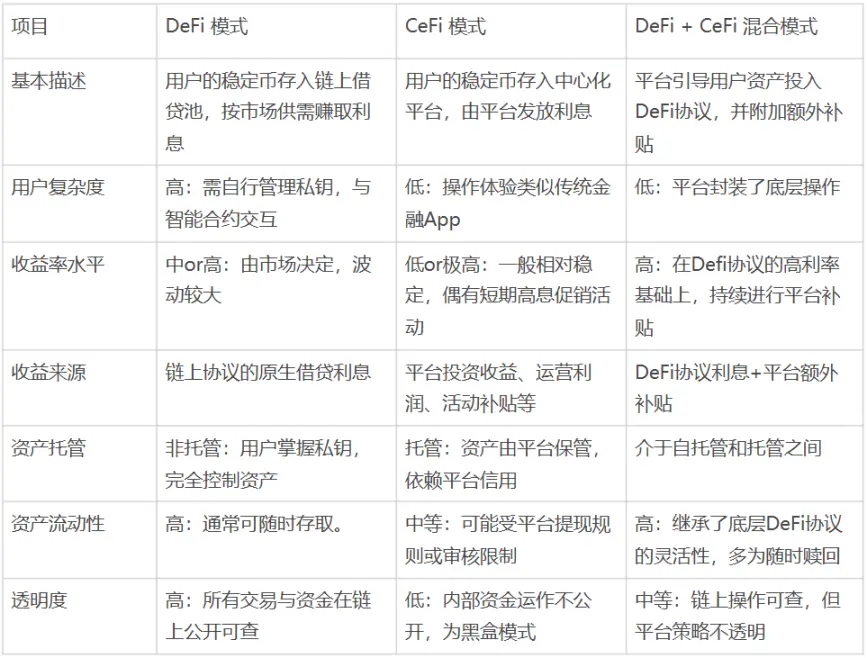
The DeFi native model: creating a completely transparent "on-chain bank." Users manage their own wallet private keys and interact directly with decentralized lending protocols like Aave and Compound. They deposit stablecoins into an on-chain pool and earn floating interest based on real-time market demand. This model offers the advantage of full user control over their assets, with all capital flows transparent and open. However, it requires high operational skills and a certain level of blockchain knowledge.
The CeFi custodial model is more similar to traditional financial products. Users deposit stablecoins on centralized platforms (such as Coinbase and Binance), which manage their assets and distribute interest. The user experience is similar to that of a mobile banking app. While this model offers convenience and ease of use, it comes at the cost of users giving up direct control over their assets. Funds operate in a "black box" fashion, relying on the platform's creditworthiness.
The Ce-DeFi hybrid model attempts to combine the advantages of both models. Through technical encapsulation, the platform directs user assets to selected underlying DeFi protocols for interest generation, while the platform itself may also provide additional income subsidies. While users enjoy the convenience of CeFi, their assets remain in their own wallets (non-custodial), achieving both high returns and asset ownership. However, this model carries the risks inherent in both the underlying DeFi protocol and the platform itself.
2. Exploring the Source of Income: How Do DeFi Lending Protocols Provide the Interest Rate Foundation for Stablecoin Investment?
After sorting out the three mainstream models, a clear conclusion emerges: if we put aside the short-term marketing activities of centralized platforms, stablecoin wealth management can provide a sustainable, high-return interest rate foundation, which is completely built on the on-chain DeFi protocol.
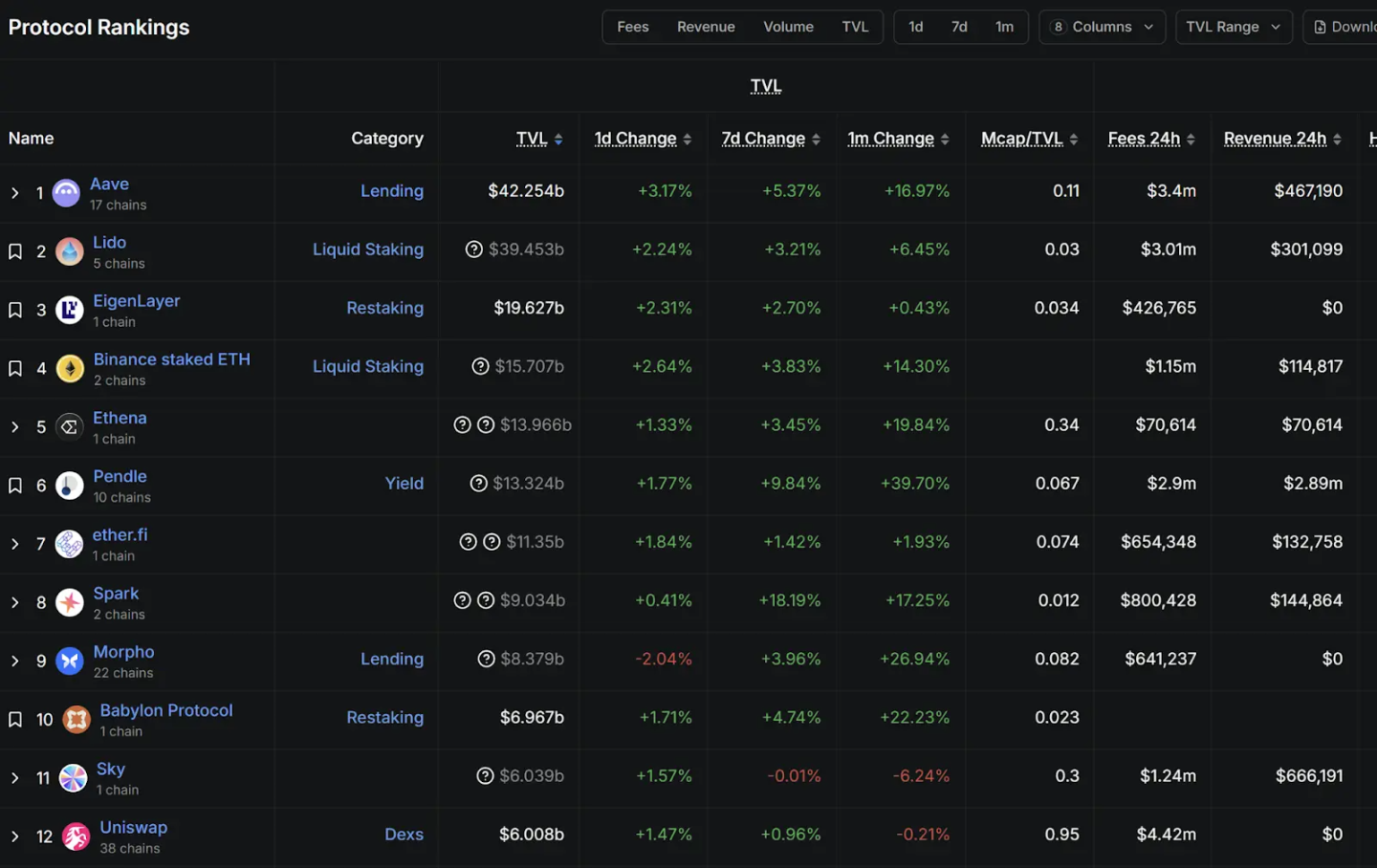
Source: DefiLlama, as of September 17, 2025
According to data from DefiLlama (as of September 17, 2025), the on-chain protocol ecosystem is highly diverse, encompassing staking, lending, re-staking, and decentralized exchanges. While their mechanisms vary, the mainstream protocols underlying stablecoin wealth management products generally employ a fundamental financial logic—earning the interest differential between lending and borrowing, a principle closely resembling the core of traditional commercial banking. Therefore, this section will analyze this typical interest-earning model using Aave, the leading DeFi lending protocol, as an example.
Aave was founded in 2017 by Finnish entrepreneur Stani Kulechov. Its predecessor was ETHLend, which later pivoted and changed its name to Aave (meaning "ghost" in Finnish). Data from DefiLlama shows that Aave's total value locked (TVL) has exceeded $40 billion, ranking first among all DeFi protocols. Its official website also states that Aave operates across 14 major networks, with net deposits exceeding $70 billion and a 30-day trading volume reaching $270 billion, making it a giant "on-chain bank."

Source: Aave official website
Aave's core business model is an efficient and transparent peer-to-peer lending market. Its robust operation and ability to consistently provide high interest rates rely on three core mechanisms:
- Overcollateralization: This is the cornerstone and safety cushion of all on-chain lending. Anyone seeking to borrow must first deposit crypto assets worth significantly more than the amount they are borrowing as collateral (for example, collateralizing $150 worth of Ethereum to borrow $100 in stablecoins). This barrier greatly protects depositors' funds and prevents bad debts from being incurred due to borrower defaults.
- Pool-to-Peer: Unlike the traditional model of matching individual borrowers with depositors, Aave pools all depositors' stablecoins into a single, massive liquidity pool. Borrowers borrow directly from the pool, and interest is paid to the entire pool. This design significantly improves fund matching efficiency and liquidity, allowing users to deposit and withdraw funds instantly without waiting for a counterparty.
- Dynamic interest rates: This is the direct source of high returns. The interest rate on the fund pool is not fixed; instead, it's adjusted in real time by an algorithm based on "fund utilization" (the proportion of funds borrowed in the pool). When market demand for lending crypto assets like BTC and ETH is strong (for example, during a bull market, when traders want to leverage long positions), large amounts of funds are lent out, increasing fund utilization. The algorithm automatically raises deposit rates to attract more stablecoin deposits, while also increasing borrowing rates. Therefore, the high interest earned by stablecoin depositors is essentially a payment to meet the strong demand from crypto asset borrowers. For example, on the actively traded Base chain, Aave's stablecoin deposit rate has long remained around 5%, a true reflection of market supply and demand.
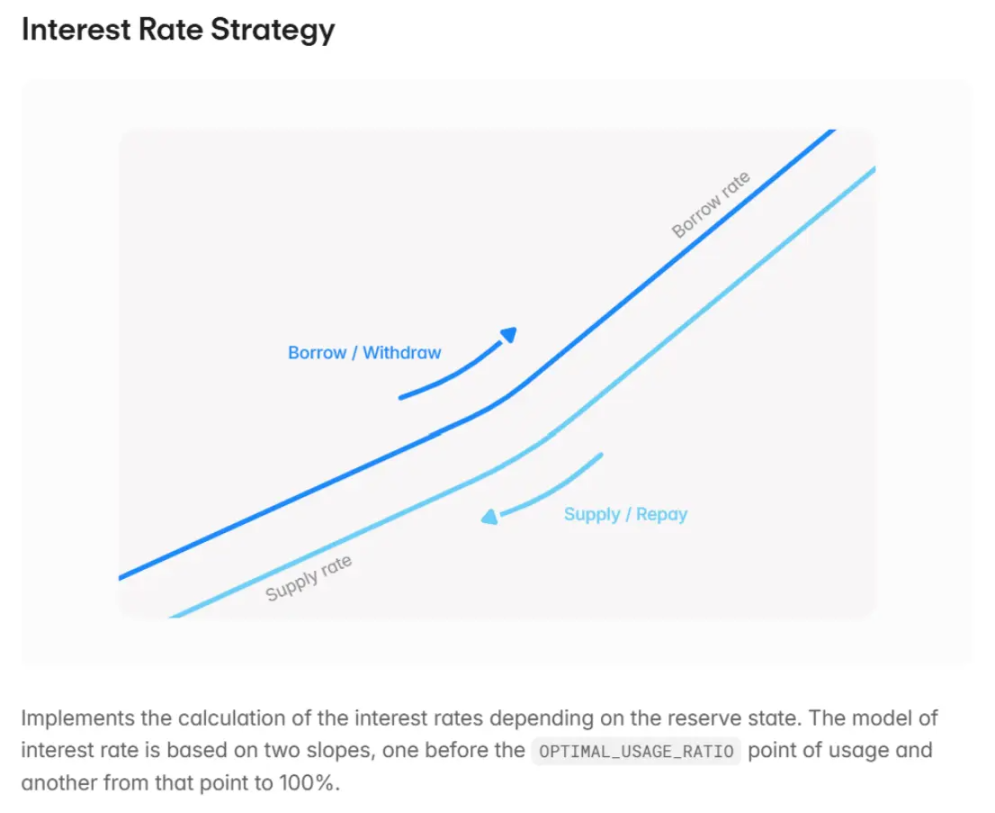
Source: Aave official documentation
This shows that the high returns of stablecoin investment are not fictional; they are rooted in the unique "non-stablecoin" lending activities in the crypto market, which are driven by high volatility and high trading demand. DeFi protocols like Aave essentially act as decentralized financial intermediaries driven by code and algorithms.
3. Both Ends of the Scale: Opportunities and Practical Considerations for Stablecoin Financial Management
Once its underlying logic is clarified, the market positioning of stablecoin investment becomes increasingly clear. It precisely addresses the core pain points of investors in the current low-interest rate environment. By investing in stablecoins pegged to the US dollar, holders can effectively avoid the volatile price fluctuations of mainstream assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum while also earning stable returns far exceeding those from traditional channels.
As shown in the table below, stablecoin investment products offer unique appeal compared to mainstream, stable dollar-denominated wealth management products. While their risk profile mirrors that of government bonds and money market funds, they prioritize principal stability, yet their potential yields are more than double those of the latter. Furthermore, they offer the liquidity of demand deposits, a very low barrier to entry, and the high transparency afforded by an on-chain model. This combination of high returns, flexibility, and transparency constitutes their core competitiveness in the current market environment.
Comparison of mainstream stable US dollar wealth management products:
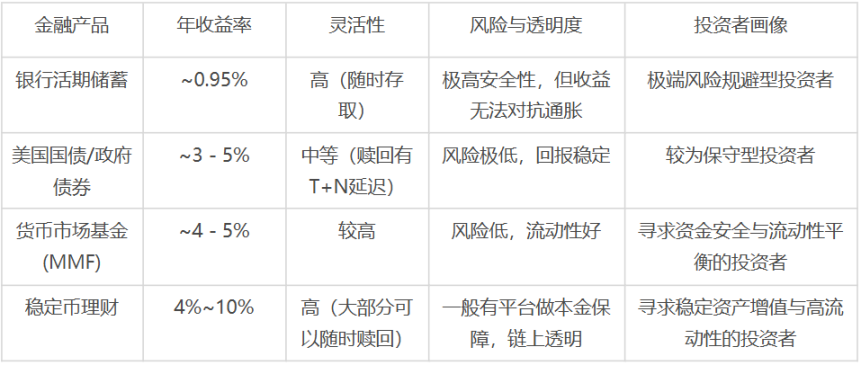
Source: Public information compilation
However, the flip side of opportunity is always risk. As the Aave official documentation states, "Decentralized access to liquidity is not without risk, but risks can be mitigated and managed." While investors are attracted by high returns, they must be aware of the following potential risks:
First and foremost is protocol security risk. This is an inherent technical risk in the blockchain world. Possible code vulnerabilities in smart contracts, oracle attacks, and cross-chain bridge security issues can all become entry points for hacker attacks. While multiple code audits and community oversight can mitigate these risks, they cannot eradicate them.
Secondly, there's the risk of extreme market fluctuations. While stablecoin wealth management products invest in stablecoins themselves, their returns stem from lending demand for mainstream crypto assets (such as Bitcoin and Ethereum). A systemic collapse in the crypto market could trigger large-scale cascading liquidations, placing significant liquidity pressure on the underlying protocol's funding pool. Such "black swan" events would severely test the protocol's risk management mechanisms.
Finally, there's the risk of stablecoins depegging themselves. History has proven that stablecoins aren't absolutely stable. Even mainstream stablecoins can temporarily deviate from their pegs due to market panic or a credit crisis at their issuers. If a systemic credit collapse similar to the Lehman Brothers collapse in traditional finance were to occur, the ripple effect on the entire ecosystem would be incalculable.
IV. Conclusion: Under the new normal of interest rate cuts, it is rational to embrace DeFi innovation
Returning to the original question posed in this article: As the Federal Reserve slowly opens the door to interest rate cuts, forcing global investors to seek new sources of income growth, DeFi innovations, exemplified by stablecoin investment, undoubtedly offer a highly attractive option. It's no longer just an experiment for a few geeks, but has gradually evolved into a financial ecosystem capable of handling large amounts of capital, operating with self-consistent logic and efficiency. It cleverly transforms the exuberant capital demand within the Web3 world into a product similar to "high-interest dollar savings" that external investors can understand and participate in, building a bridge between traditional investors and decentralized finance.
Of course, we must face the reality that this "new world" is still under construction, with both opportunities and risks. For ordinary investors, the correct approach is not to blindly rush in, nor to throw the baby out with the bathwater. Instead, the correct approach is to fully understand the sources of returns and potential risks, and to rationally consider it as a worthy new option in diversified asset allocation. Only by facing and learning to manage these risks deeply embedded in technology and the market can this emerging financial sector truly prosper and achieve long-term success, and can the innovative light of DeFi "reach the homes of ordinary people."