By ZachXBT
Compiled by Azuma, Daily Planet
Editor's Note: North Korean hackers have always been a major threat to the cryptocurrency market. In the past, victims and industry security professionals could only infer North Korean hackers' behavior patterns by reverse engineering related security incidents. However, yesterday, renowned on-chain detective ZachXBT, in a recent tweet, cited an investigation and analysis by a white-hat hacker who reverse-hacked North Korean hackers. This proactive analysis reveals the North Korean hackers' working methods for the first time, potentially providing positive insights into preemptive security measures for industry projects.
The following is the full text of ZachXBT, compiled by Odaily Planet Daily.
An anonymous hacker recently compromised the device of a North Korean IT worker, revealing how a five-person technical team operated over 30 fake identities, using fake government-issued IDs and purchased Upwork and LinkedIn accounts to infiltrate various development projects.
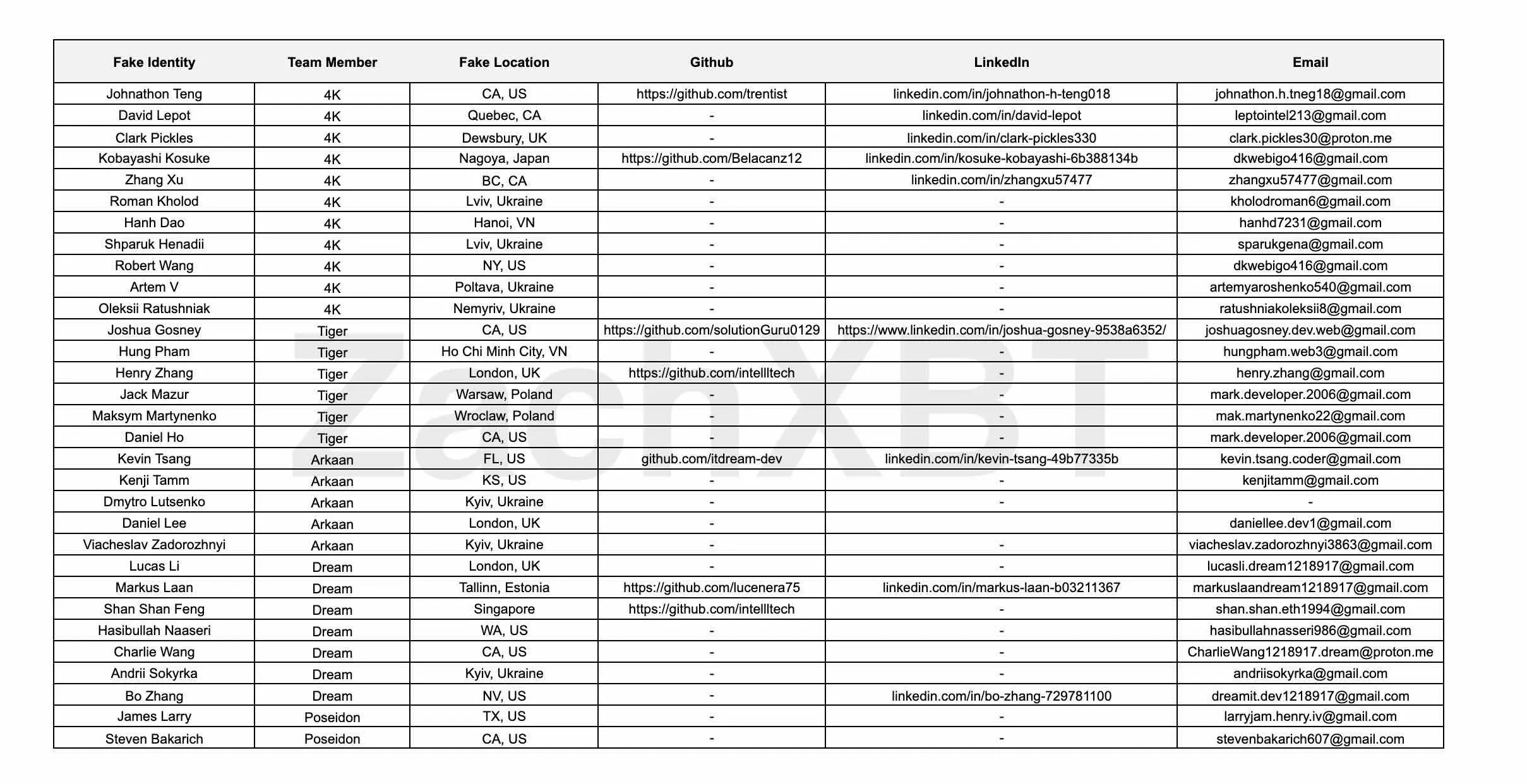
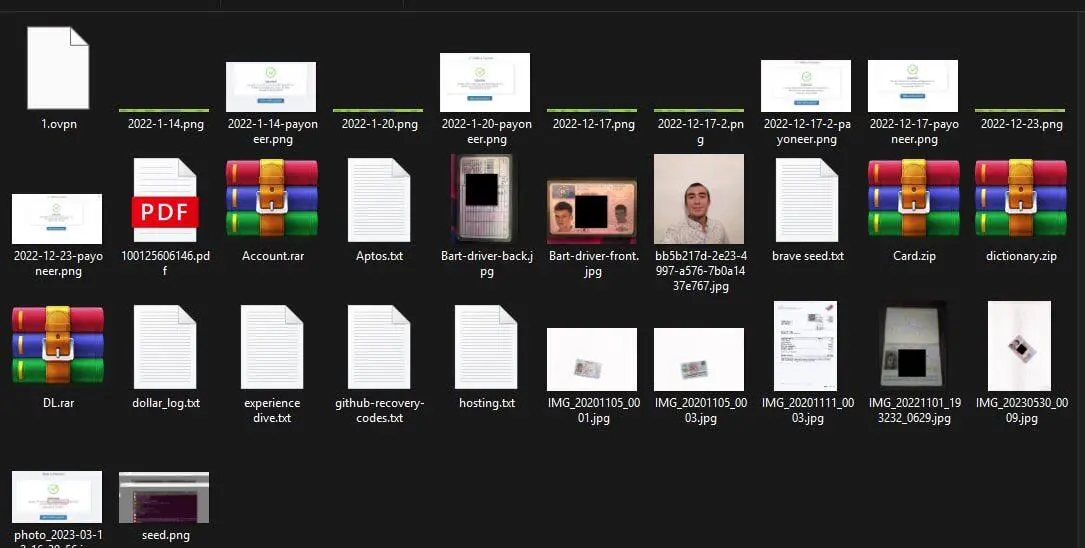
Investigators obtained Google Drive data, Chrome browser profiles, and device screenshots, which revealed that the team relied heavily on Google tools to coordinate work schedules, assign tasks, and manage budgets, with all communications conducted in English.
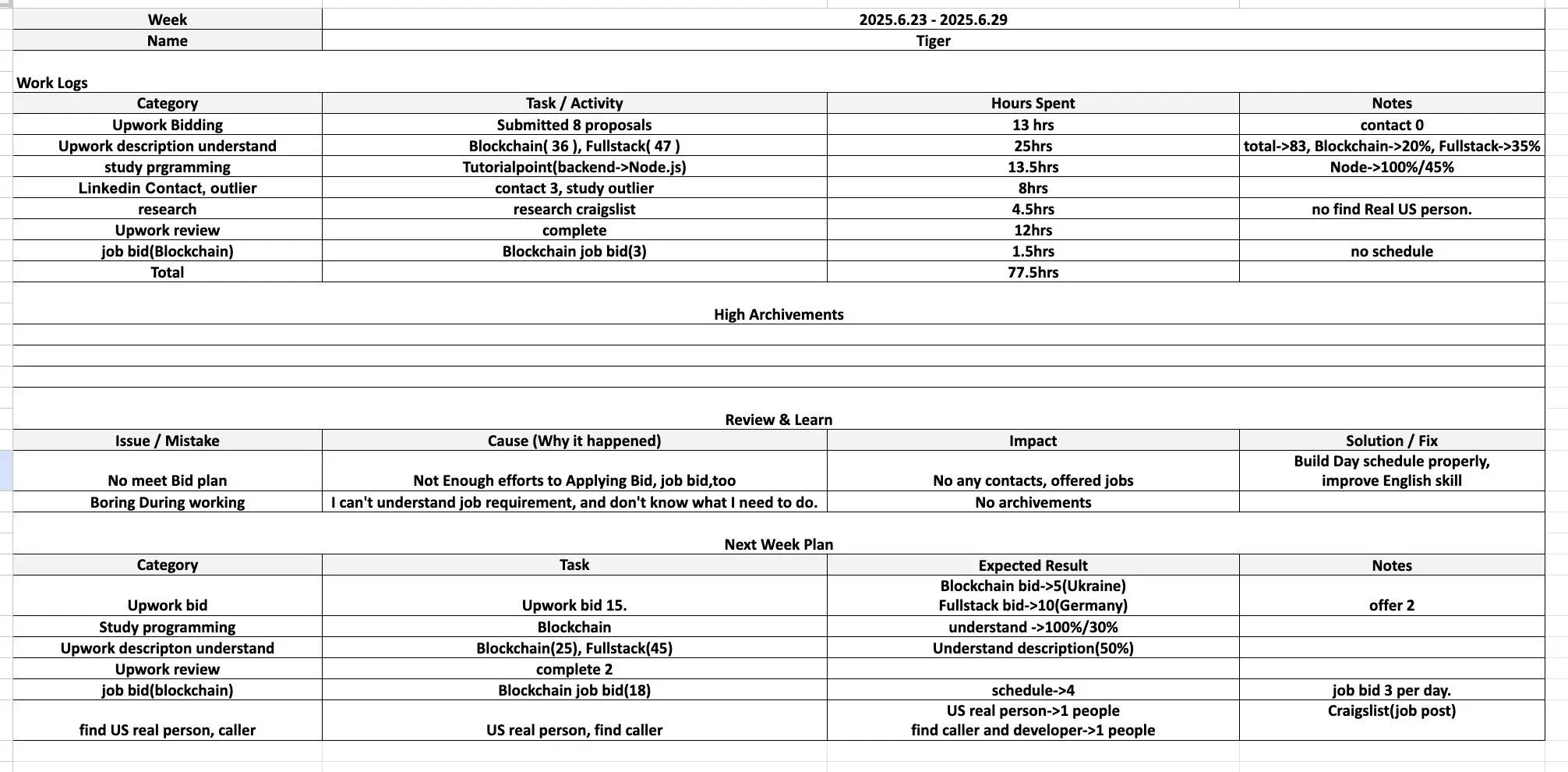
A weekly report from 2025 revealed the hacker team's work patterns and the difficulties they encountered. For example, one member complained about "not understanding the job requirements and not knowing what to do," but the corresponding solution was to "dedicate yourself and work harder."
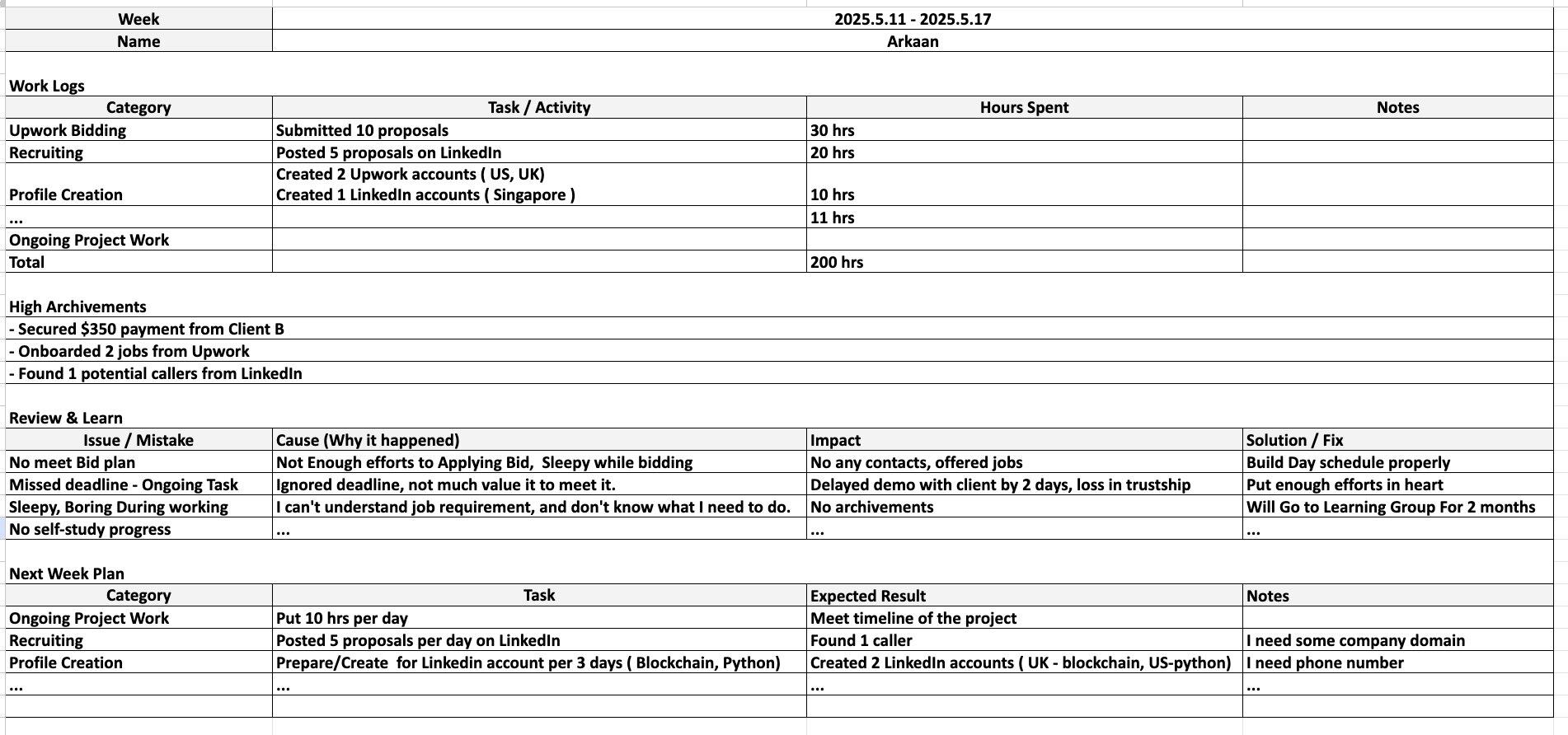
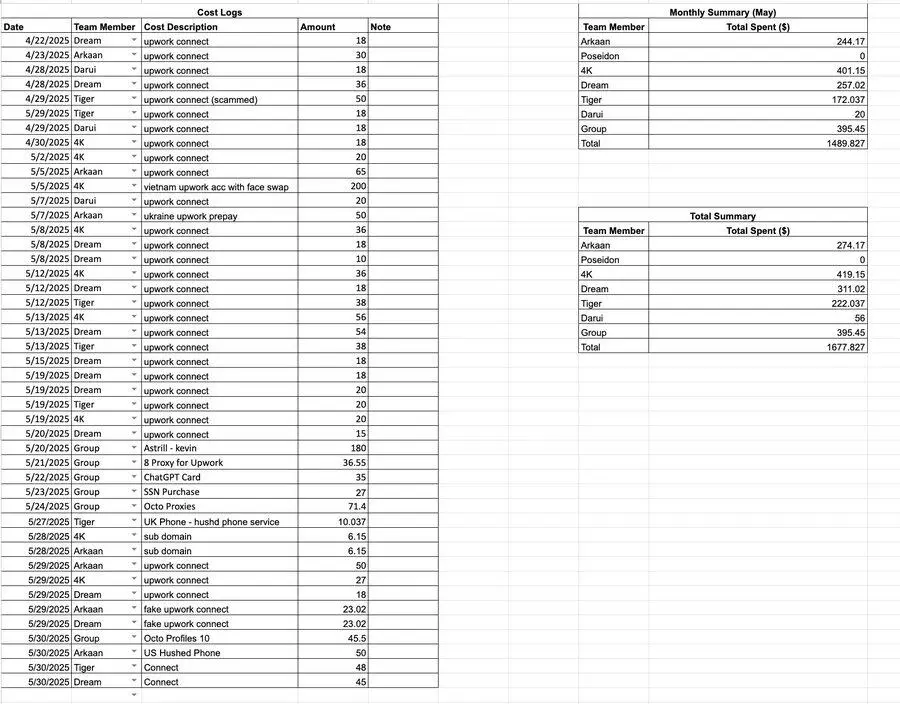
Detailed expense records show that their expenditure items include purchasing social security numbers (SSNs), Upwork and LinkedIn account transactions, renting phone numbers, subscribing to AI services, renting computers, and purchasing VPN/proxy services.
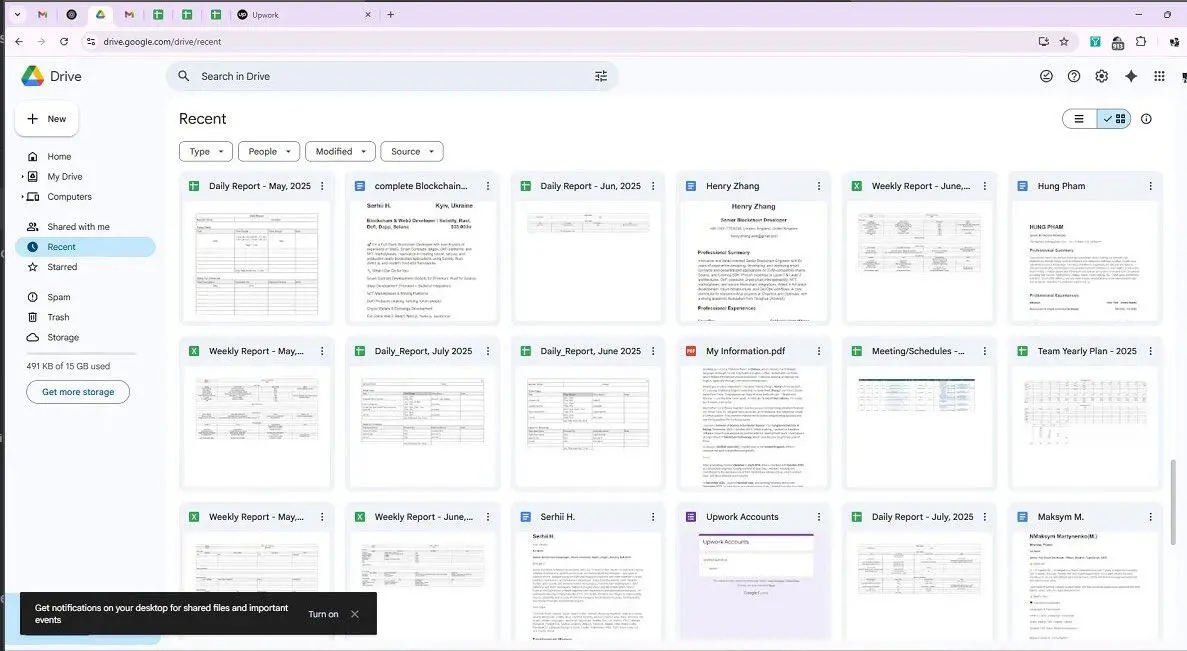
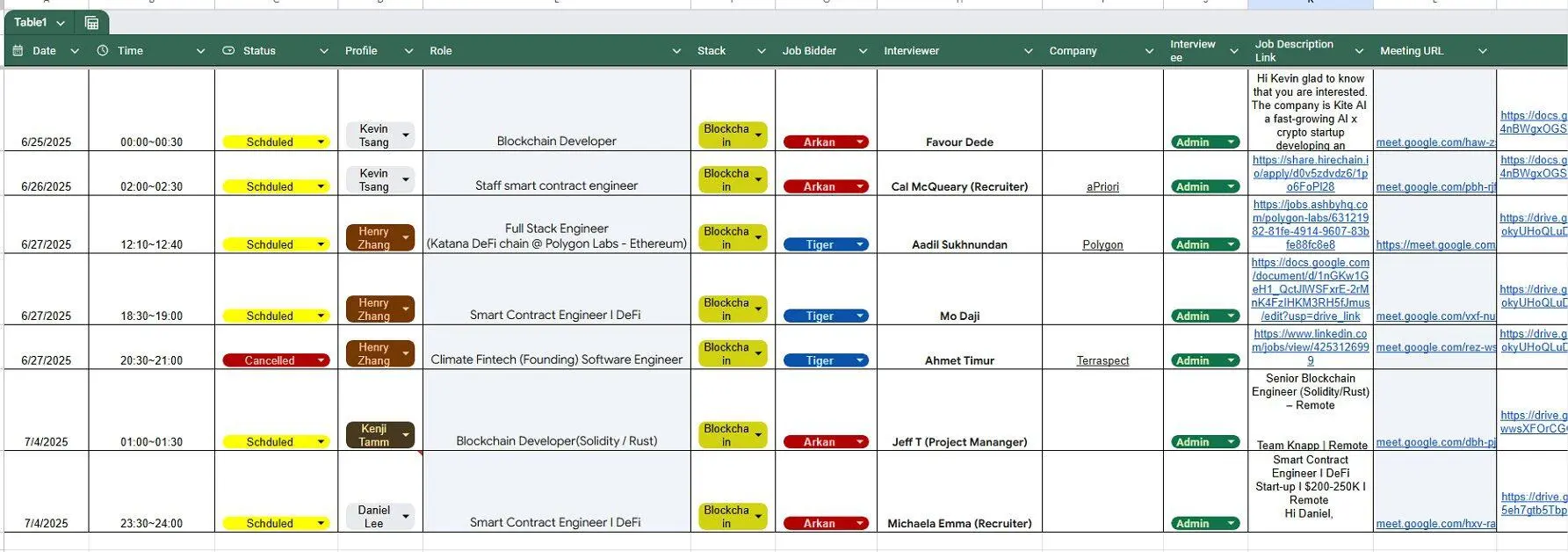
One spreadsheet detailed the schedule and scripts for meetings attended by the fictitious "Henry Zhang." The process revealed that these North Korean IT workers would first purchase Upwork and LinkedIn accounts, rent computer equipment, and then complete outsourced work using the AnyDesk remote control tool.

One of the wallet addresses they use to send and receive funds is:
0x78e1a4781d184e7ce6a124dd96e765e2bea96f2c;
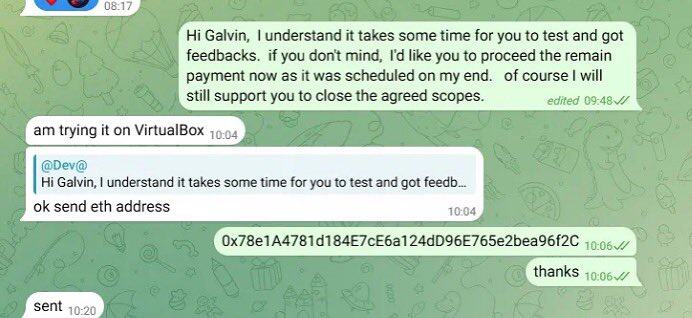
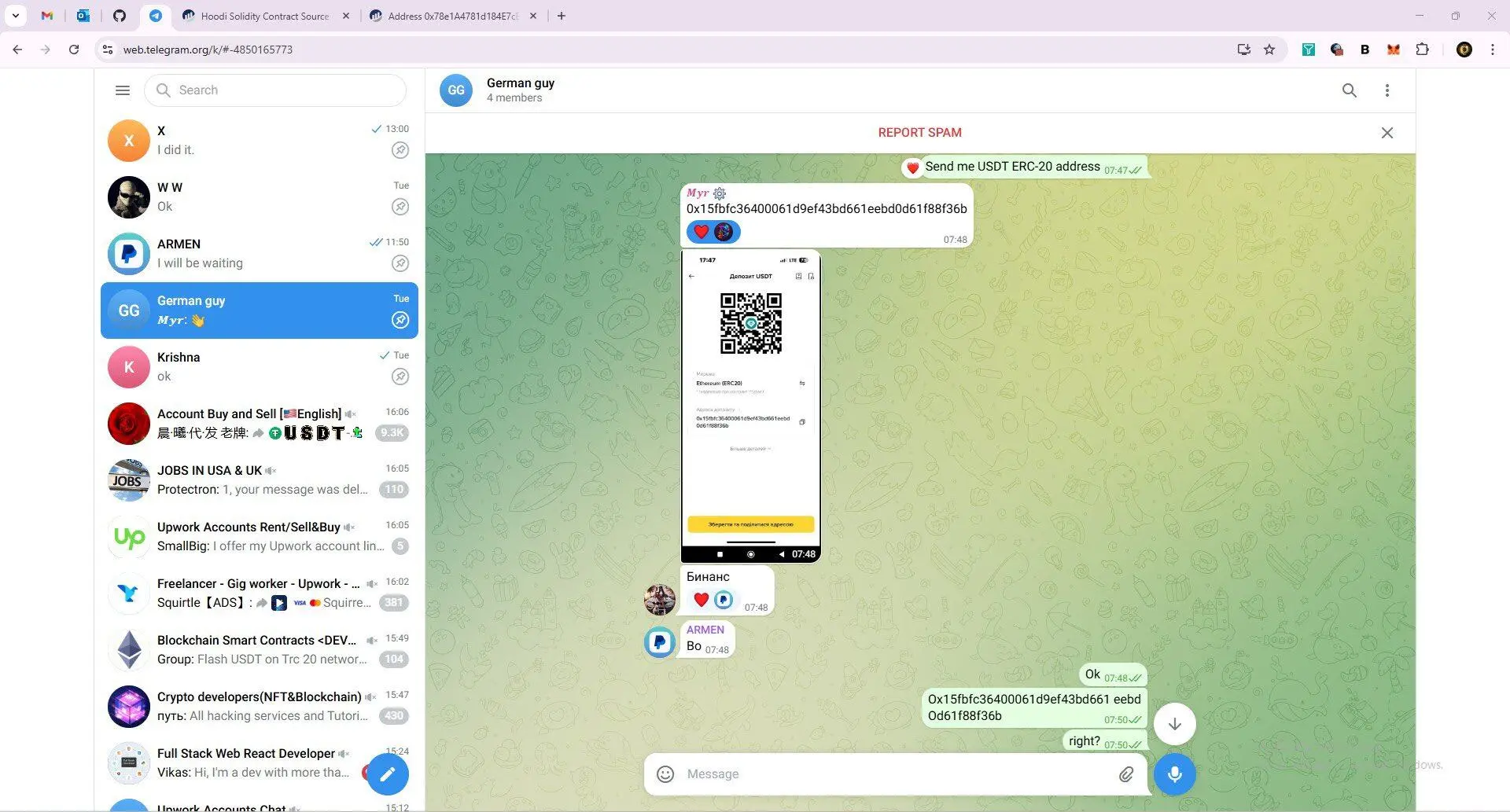
This address is closely linked to the $680,000 Favrr protocol attack in June 2025. Its CTO and other developers were later confirmed to be North Korean IT workers with forged credentials. This address has also been used to identify North Korean IT personnel involved in other infiltration projects.
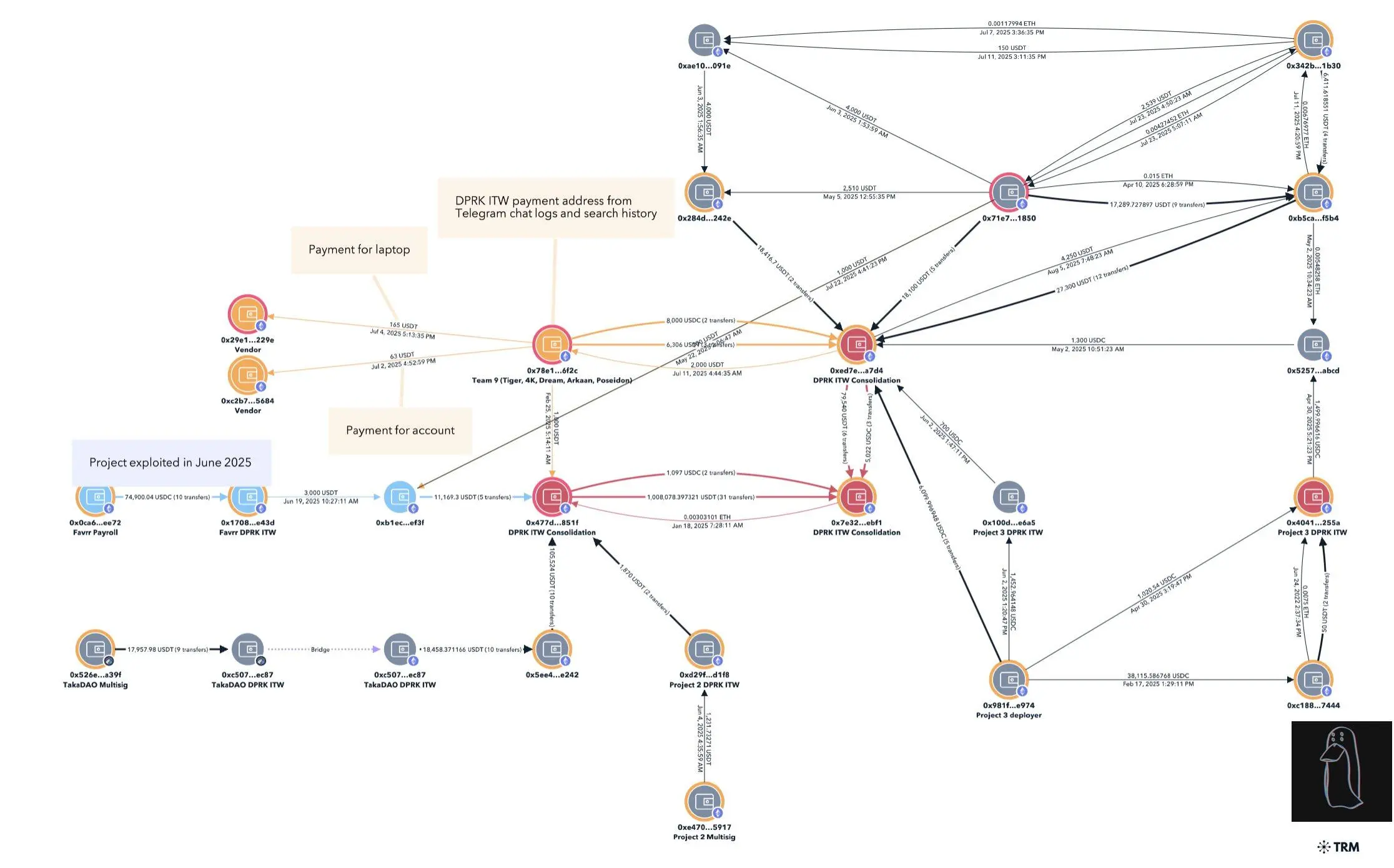
The team also found the following key evidence in their search records and browser history.
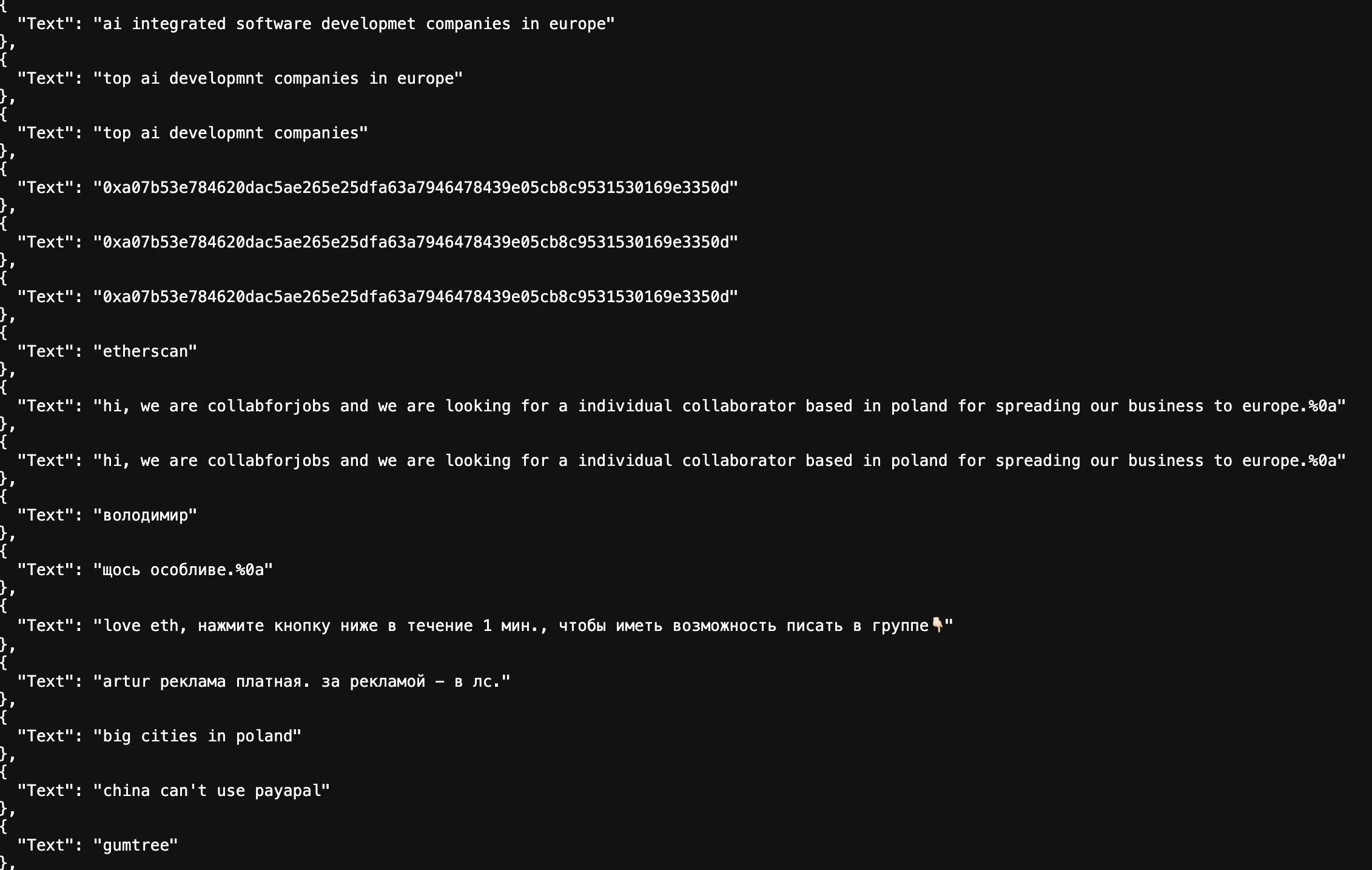
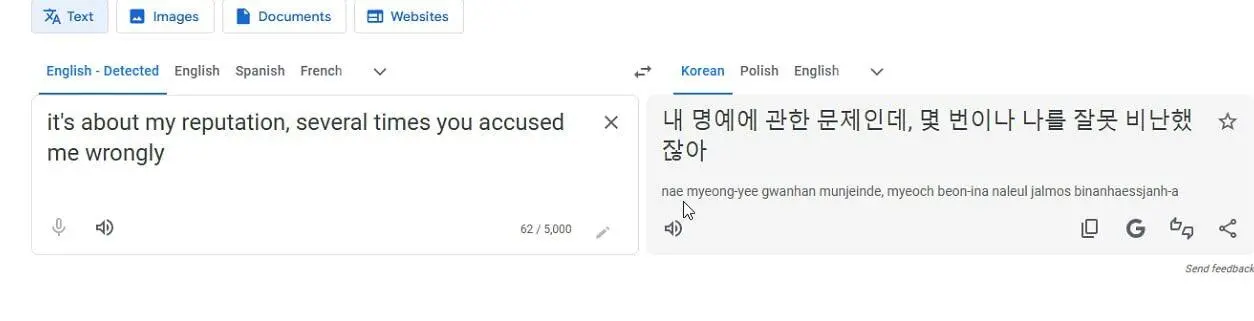
One might ask, “How can we be sure they are from North Korea?” In addition to all the fraudulent documents detailed above, their search history also shows that they frequently use Google Translate and translate into Korean using a Russian IP.
Currently, the main challenges for enterprises in preventing North Korean IT workers are as follows:
- Lack of systematic collaboration: There is a lack of effective information sharing and cooperation mechanisms between platform service providers and private enterprises;
- Employer oversight: Hiring teams often become defensive after receiving risk warnings, or even refuse to cooperate with investigations;
- Impact of numerical advantage: Although its technical means are not complicated, it continues to penetrate the global job market with its huge base of job seekers;
- Funding conversion channels: Payment platforms such as Payoneer are frequently used to convert fiat currency income from development work into cryptocurrency;
I have introduced the indicators that need attention many times. If you are interested, you can check out my historical tweets. I will not repeat them here.







