By Josiah Makori
Compiled by: Vernacular Blockchain
What is crypto narrative?
Crypto narratives refer to popular ideas, stories, or beliefs in the cryptocurrency space that influence people's views and value judgments on cryptocurrencies. They can influence investor sentiment, market trends, and the adoption of new technologies.
Key Takeaways
Crypto narratives refer to popular ideas, stories, or beliefs in the cryptocurrency space that influence people's views and value judgments on cryptocurrencies and can influence investor sentiment, market trends, and the adoption of new technologies.
One of the most important trends for 2024 is the focus on accessibility, where anyone can participate without the need for in-depth knowledge of cryptocurrencies and blockchain. This is reflected in the popularity of memecoins and prediction markets.
Narratives worth watching in 2024 include: Memecoins, Liquid Restaking Tokens, Liquid Staking Derivatives, Blockchain Modularity, Layer 1, Layer 2 (Optimistic rollup and zero-knowledge rollup), BRC-20, Decentralized IoT Network (DePIN), Telegram crypto trading bots, Prediction Markets, and Real Asset Tokenization (RWAs).
Crypto narratives can also be misleading or even harmful, especially when built on false assumptions or excessive hype. Therefore, it is important to critically evaluate narratives and make investment decisions based on solid analysis and research.

Market participants are always looking for trends to better understand what is happening in the current market, why it is happening, and its potential impact. Historically, they usually predict the future market environment in advance through the dynamic performance of market cycles. From Elon Musk's tweets driving DOGE price fluctuations to believing that Bitcoin halving will bring a bull market every four years, many investors predict price movements through the market narrative of cryptocurrencies.
For example, the narrative of cryptocurrency as a “store of value” attracts many investors who see it as a hedge against economic uncertainty. Similarly, the narrative of blockchain as a “disruptive technology” attracts many entrepreneurs and developers who are committed to developing new applications on the blockchain.
1. What is crypto narrative?
This article was updated by the Coingecko team in January 2024 to reflect new and emerging crypto narratives.
Market participants always seek trends to better understand what is happening in the current market, why it is happening, and what impact it may have. Historically, people use the dynamics of market cycles to take more proactive actions in future market environments. From Elon Musk's tweets driving DOGE price fluctuations to the belief that Bitcoin halving will bring a bull run every four years, many investors predict price movements through crypto narratives.
For example, the narrative of “cryptocurrency as a store of value” has attracted many investors who believe that cryptocurrencies can be used as a hedge against economic uncertainty. Similarly, the narrative of “blockchain as a disruptive technology” has attracted many entrepreneurs and developers who are committed to developing new applications on blockchain.
Why do crypto narratives matter?
Crypto narratives emerge from a variety of factors, including the technical capabilities of crypto and blockchain, social and economic events, and the beliefs and motivations of individuals in the cryptocurrency industry. Mainstream media, social media, online forums, influencers, and market trends can all drive narrative formation. In 2024, we see more and more narratives exploring the capabilities and applications of blockchain, such as the Decentralized IoT Infrastructure Network (DePIN). However, there are also narratives like memecoins and prediction markets that are rapidly emerging. These narratives make crypto markets more accessible to anyone because they do not require a deep understanding of the crypto space.
Narratives are important because they play a major role in shaping public perception and subsequent market movements. They provide a framework for understanding the potential risks and rewards of different types of cryptocurrencies and can influence the trajectory of the entire cryptocurrency industry.
However, crypto narratives can also be misleading or even harmful due to false assumptions or excessive hype. Therefore, it is very important to critically evaluate these narratives and make investment decisions based on solid analysis and research.
Today, multiple emerging trends and themes are attempting to define 2024. In this guide, we’ll cover the top crypto narratives to watch in 2024:
2. Memecoins
Memecoins remain one of the most profitable narratives in 2024, and market expectations for a memecoin supercycle are heating up. CoinGecko data shows that SPX6900 and Gigachad are at the top of the list of gainers in the third quarter. In addition, there are other memecoins that have reached new heights, such as GOAT becoming the first Pump.funToken to break $1 billion in market value. As of the time of writing, the total market value of memecoins has reached $107.5 billion.
As the name implies, memecoins are based on internet memes and popular trends, supported by passionate communities. They are often positioned as entertainment tokens that rely on growing communities to achieve virality and growth. Memecoins also provide traders with an easy way to participate in the hype of hot blockchains, as such tokens are usually sold for just a few cents when issued. Unlike other narratives, potential buyers do not need to have a deep understanding of the world of cryptocurrency to join the hype, as most memecoins have little practical use when issued.
2024 also gave rise to the meme coin generator, which simplified the token creation process and enabled anyone to issue their own meme coin without a technical background. The biggest player in this field is Pump.fun based on Solana. As of now, more than 3 million tokens have been issued on Pump.fun, with a total revenue of more than $187 million.
As of the time of writing, Solana and Base are among the most popular blockchains for memecoins.
3. Prediction Markets
Prediction markets allow users to bet on ongoing and future events using cryptocurrency, where users can purchase shares for “yes” or “no.” Once the event is over, users who choose the correct option will receive a payout based on the number of shares purchased.
Of these prediction markets, Polymarket is the largest, with its most recent “2024 Presidential Election Winner” prediction having traded over $732 million. Other popular prediction market categories include sports, business, and pop culture.
4. Liquid Restaking Tokens
Restaking is an increasingly popular narrative that focuses on improving capital efficiency by enabling users to use the same token to stake simultaneously on different protocols, providing security for multiple networks. This mechanism helps protocols solve the challenges of building their own validator clusters while providing scalable security based on the needs of the respective protocols. In return, restakers can earn additional rewards through their restaking strategies (but also face additional slashing risks).
EigenLayer is a pioneer in the re-staking space, with a total locked value (TVL) of over 3.5 million ETH as of this writing. Users can re-stake their liquid stake tokens such as stETH, rETH, and cbETH on EigenLayer to provide security for the Active Verification Service (AVS).
You can view the top liquid re-staking tokens on Coingecko.
5. Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs)
Liquid staking derivatives are cryptocurrencies issued by liquid staking platforms that allow stakers to unlock their liquidity-restricted staked assets and earn more returns. In standard staking, stakers provide security for the Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain by depositing assets in the protocol. However, this approach leads to capital inefficiency because stakers' assets are locked and cannot generate additional returns.
Liquid staking comes into being in this context. The value of derivative assets is linked to the underlying assets (assets locked when staking on the proof-of-stake blockchain), and accumulates rewards and continues to increase in value over time. At the same time, derivative tokens can be used for other DeFi activities, such as lending and providing liquidity. In return, most liquid staking providers will extract a 5-10% share of the staking rewards as income.
Liquid staking derivatives solve the problem of capital inefficiency, lower the entry barrier to staking, and improve the security and stability of the network.
You can view the top liquid staking tokens on Coingecko.
6. Blockchain Modularity
Early blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, were monolithic structures, meaning that the blockchain was required to perform all tasks. However, as the focus of competition shifted from performance to cost and flexibility, the modular era of blockchains gradually arrived. Modularity splits blockchains into independent components, enabling blockchains to break through current expansion limitations.
Modular components include:
- Execution layer: responsible for transaction execution
- Settlement: responsible for settlement, fraud proof and connecting other execution layers
- Consensus: responsible for reaching consensus on the order of transactions
- Data Availability Layer: Provides accessible data to all network participants
Transaction execution usually occurs on the second layer (Layer 2) chain, such as Optimism and Arbitrum, which is responsible for executing transactions and sending packaged transactions to the main chain. In addition, the second layer chain itself is also gradually modularized, such as OPStack, which modularizes all elements of the second layer chain into standardized open source modules that developers can use to create new blockchains.
Meanwhile, EigenDA is a decentralized data availability layer built on Ethereum and is currently used by Layer 2 chain Mantle to provide data availability support.
Layer 1 blockchains like Celestia are also adopting modular architectures. In Celestia’s case, the focus is on consensus and data availability, optimizing storage. This allows Layer 2 chains built on Celestia to focus on building the best execution environment for their applications.
6. Layer 1s
Layer 1 (L1) blockchains are the infrastructure on which other blockchain applications, such as smart contracts, are built. They execute most on-chain transactions and serve as the "source of truth" for public blockchains. Traditional L1 blockchains, such as Ethereum, often face problems such as slow transaction speeds, low scalability, and high fees. At this time, second-layer blockchains (Layer 2s) emerge to execute transactions, allowing L1 to focus on issuing and verifying these transactions. However, new L1 networks are changing the landscape in terms of transaction speed, cost, and interoperability.
Here are some notable L1 projects that are gaining attention as the L1 narrative heats up:
1) Solana
Despite launching in 2020, Solana’s ecosystem has become the most popular blockchain ecosystem in 2024, accounting for 38.8% of crypto investors’ on-chain narrative-specific interest. A major reason for the Solana ecosystem’s popularity is the current memecoin wave, with Solana’s high speed and low fees, coupled with the virality of the memecoin generator Pump.fun, making it one of the leading chains for memecoin speculation.
2) Sui
Sui is an "infinite platform" for building rich and dynamic on-chain assets from games to finance. It is the first permissionless L1 network designed from the ground up for creators and developers, dedicated to serving the upcoming billion Web3 users. Sui was created by Mysten Labs, a former Meta engineering team.
Sui scales horizontally to meet application needs, increasing scalability without limit while ensuring that transaction costs are economical. In addition, it significantly improves scalability and supports parallel consensus for simple transactions such as NFT casting and transfer. Complex transactions such as asset management and DeFi applications are handled by the DAG-based Narwhal and Bullshark memory pools and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus mechanism.
7. Second layer: Rollups
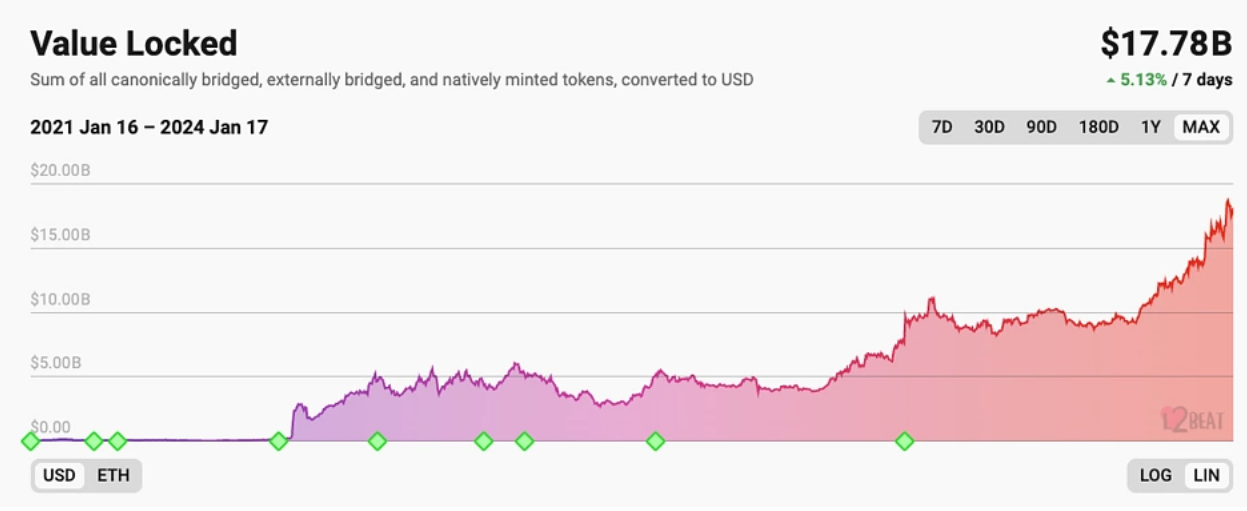
The vertical scaling narrative focuses on the second layer (L2), which are protocols built on top of L1 to further scale and enhance them. L2 significantly increases transaction throughput by moving transactions off-chain, significantly reducing the computational burden of L1. The total value locked (TVL) of L2 has steadily increased, maintaining strong performance even in the face of negative sentiment in the DeFi market and the overall crypto market.
A. Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic Rollups are L2 scaling solutions that aim to increase transaction throughput and reduce fees while maintaining the security of the underlying blockchain. They use a trust-based model to confirm transactions off-chain, and are confirmed by a small group of "witnesses" before being added to the underlying blockchain.
Source: Beat
Here are some L2 Optimistic Rollups projects worth keeping an eye on in 2024:
1) Base
In February 2023, Coinbase launched Base, an L2 blockchain built with Optimism's OP Stack, designed to serve the upcoming millions of Web3 users and build on Coinbase's massive user base. The Base network provides creators with a secure, low-cost, and developer-friendly solution to build Web3 applications. Since its launch, Base has continued to grow in popularity, with increased investor interest in 2024 making it the second most popular chain after Solana. Base is also popular among memecoin traders, with its top memecoin BRETT having a market cap of over $1 billion.
2) Arbitrum
Arbitrum is an L2 scaling solution that leverages Optimistic Rollups, designed to achieve high throughput and reduce transaction costs for users. Even after the Ethereum merger (The Merge), Ethereum's speed and gas fees are still higher than other networks such as Arbitrum. This has led many Web3 users and creators to turn to the Arbitrum network, pushing its total locked value (TVL) to a high of $3.2 billion in November 2021.
The recent ARB airdrop has injected a lot of liquidity into the Arbitrum network. Many users who received ARB tokens were incentivized to use these tokens to trade, stake, or provide liquidity for various decentralized trading platforms and protocols on the Arbitrum network. This airdrop also helped increase the visibility of the Arbitrum network and demonstrated its potential as an Ethereum L2 scaling solution.
3) Optimism
Optimism is positioned as a "fast, stable, and scalable L2 protocol designed by Ethereum developers for Ethereum developers." It is built as a minimal extension of the current Ethereum blockchain to seamlessly expand Ethereum applications. Unlike common EVM-compatible chains, Optimism is EVM-equivalent, which means that Optimism fully complies with the formal specifications of the Ethereum blockchain and runs in sync with Ethereum. Optimism also launched OPStack to standardize the various modular elements of the L2 chain so that developers can build new chains that interoperate with Optimism. According to Deflama data, Optimism's TVL reached an all-time high of US$1.15 billion in August 2022.
B. Layer 2: ZK Rollups
Zero-knowledge rollups (ZKRollups) are a Layer 2 scaling solution that improves Layer 1 throughput by moving computation and state storage off-chain. They batch large numbers of transactions and publish summary data on-chain. The core of ZK Rollups is the ability to prove knowledge of something without revealing information. Therefore, they are very attractive in privacy-sensitive application scenarios, such as digital identity verification and confidential transactions.
Here are some ZK Rollups projects worth watching in 2024:
1) zkSync Era
zkSync Era is an L2 aggregation scheme that uses zero-knowledge proofs to expand the Ethereum network without sacrificing its security and decentralization. zkSync Era stores most of the computation and data off-chain, allowing users to enjoy the security of Ethereum while getting higher transaction speeds and lower transaction costs.
2) Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM will be launched on Mainnet Beta on March 27, 2023, which is an important step in promoting Ethereum expansion and achieving mainstream Web3 adoption. Similar to Optimism, Polygon zkEVM is EVM equivalent, which means that most Ethereum native applications can run directly on zkEVM without developers having to modify or reimplement the code.
3) Scroll
Scroll is an L2 solution dedicated to achieving infinite scalability, high throughput, full decentralization, and trust-minimized privacy. It achieves this goal by combining ZK Rollup and a high-performance on-chain decentralized system.
4) Taiko
Taiko is a ZK Rollup Layer 2 that aims to be the closest to Ethereum equivalence, providing dApps with a scalable and efficient platform without making any changes to the existing protocol. Unlike many other ZK Layer 2s, Taiko focuses on achieving full compatibility with Ethereum rather than pursuing ZK proof generation speed, which allows developers to reuse execution clients without major adjustments. Users can experience Taiko's functionality firsthand by participating in the protocol usability test on the Taiko testnet.
8. Bitcoin Layer 2
Similar to other Layer 2s, the Bitcoin Layer 2 project attempts to expand the Bitcoin blockchain by developing an execution layer that provides higher throughput and more operations than the main network. Layer 2 on the Bitcoin network provides an execution layer different from the main network, supporting operations such as virtual machines (such as EVM) and smart contracts. However, the Bitcoin Layer 2 network faces some challenges, such as ensuring a secure cross-chain bridge between Bitcoin and its Layer 2 network, and maintaining high speed and low cost when settling proofs on the Bitcoin network.
Layer 2 on the Bitcoin network includes state channels (such as the Bitcoin Lightning Network), sidechains (such as Stacks and Rootstock), and even Rollups like Merlin.
Bitcoin: Ordinals, BRC-20 Tokens and Runes
Ordinals is one of the latest hot trends on Bitcoin. In January 2023, software engineer Casey Rodarmor deployed the Ordinals protocol on the Bitcoin blockchain, making it possible to mint NFTs on the mainnet. This move has caused different reactions in the Bitcoin community. Some people think that this will pose a threat to the Bitcoin blockchain, while others are excited about it and began to create works called "Inscriptions" - the Bitcoin version of NFTs.
Similar to NFTs, Ordinal Inscriptions are digital assets recorded on one Satoshi (the smallest unit of Bitcoin). However, unlike NFTs, which use a decentralized file storage system, Ordinals are stored directly on-chain. These inscriptions are made possible thanks to the Taproot upgrade introduced to the Bitcoin blockchain in November 2021.
The number and sequence of BTC Ordinals are closely watched, and there have been some notable series and high-priced sales, including Ordinal Punks, Taproot Wizards, Bitcoin Rocks, Timechain Collectibles, Ordinal Loops, Ripcashe's Power Source, Bitcoin Shrooms, The Shadow Hats, The Dan Files, and Toruses.
In addition to Ordinals, BRC-20 Token has also attracted much attention. BRC-20 Token uses Ordinals inscription technology to realize the function of minting and transferring homogeneous tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain. BRC-20 Token is similar to the ERC-20 standard on Ethereum and EVM networks. It is minted by the community. Once BRC-20 Token is deployed, Ordinal wallets can freely mint these tokens. Although it is still in its early stages, some platforms already support the decentralized minting and trading of BRC-20 Token.
In 2024, with the fourth Bitcoin halving, Rodarmor will launch a new homogenous token protocol for the Bitcoin ecosystem, which will make it easier and more efficient for users to create tokens on Bitcoin. Runes may take advantage of the popularity of meme coins. Rodarmor even said that "99.9% of homogenous tokens are scams and jokes." However, with this more efficient protocol, it is expected to bring significant transaction fee income, developer attention, and user growth to Bitcoin.
9. Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN)
DePIN refers to a decentralized physical infrastructure network that uses blockchain and token rewards to develop real-world infrastructure, covering wireless connectivity, geospatial mapping, travel, health, energy and other fields.
DePIN aims to create resource-efficient physical infrastructure by incentivizing providers to invest their physical resources into a decentralized network. DePIN then provides these resources to users seeking relatively low service fees, and the network generates revenue through fees paid by users.
View popular DePIN Tokens on CoinGecko.
10. Real World Assets (RWA)
Real World Assets (RWAs) refer to assets that exist in the real world or off-chain, which are transferred to the chain through tokenization to serve as a source of income in DeFi. Such assets include real estate, precious metals, commodities, and art. RWAs are a core component of the global financial system; for example, the global real estate valuation reached $326.5 trillion in 2020, while the total market value of the gold market was $12.39 trillion. More and more RWA projects are turning their attention to US Treasuries and high interest rates to provide investors with lower risk returns, including companies like Ondo Finance.
MakerDAO has also entered the RWA space, putting idle assets into short-term bonds and using the proceeds to drive the MKR buyback program and increase the DAI savings rate, which is a typical case of the protocol benefiting from RWA investment. MakerDAO shows how value flows back to token holders, and its buyback program drives MakerDAO's growth.
RWA has a huge potential impact on DeFi:
- They can provide a sustainable and reliable source of income for DeFi because they are backed by traditional assets.
- They can help DeFi become more compatible with traditional financial markets, ensuring greater liquidity, capital efficiency, and investment opportunities.
- They are able to bridge the gap between DeFi and traditional finance (TradFi).
Maple Finance (MPL), Goldfinch (GFI), and Centrifuge (CFG) are other projects focused on RWA lending that are worth a look.
Check out popular RWA Tokens on CoinGecko.
11. Telegram trading bot
In 2023, the use of Telegram cryptocurrency trading bots has surged, providing users with the convenience and efficiency to execute transactions. Users do not need to connect their computers to their wallets and approve transactions. They can purchase tokens by simply copying and pasting the contract address of the token and sending it to the chat. This also speeds up the selling process because transactions can be pre-approved and signed.
Some Telegram trading bots also have additional features, such as multi-wallet buying, which can bypass the single wallet limit of tokens; and liquidity buying functions, which immediately execute buy orders when liquidity is detected to maximize the benefits of new tokens.
Check out our article on Top 5 Telegram Trading Bots to learn more about the features of different Telegram crypto trading bots.
12. Summary
In 2023, we see narratives like AI, Chinese Tokens, and decentralized social media, as well as Layer 1, Layer 2, Liquid Collateralized Derivatives, Real World Assets, Bitcoin Ordinals, and BRC-20. Looking ahead to 2024, emerging narratives include Restaking, DePIN, DeSci, GambleFi, and a focus on blockchain modularity.
Please remember that this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Do your own research (DYOR) before investing in any asset.