Author: Kong & Lisa
Editor: Liz
background
On May 28, SlowMist detected potential suspicious activities related to Cork Protocol and issued a security alert, advising users to be vigilant and pay attention to the security of their accounts and funds.
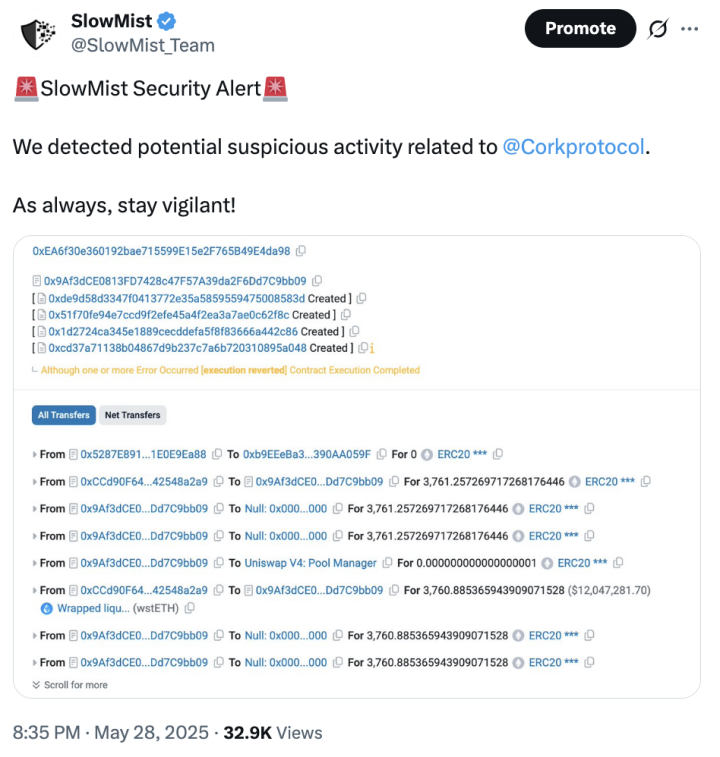
(https://x.com/SlowMist_Team/status/1927705256915333359)
Soon after, Cork Protocol issued an announcement stating: “Today at 11:23 UTC, a security incident occurred in the wstETH:weETH market. To prevent the risk from expanding, Cork has suspended all other market transactions, and no other markets are currently affected. The team is actively investigating the cause of the incident and will continue to update relevant progress.”
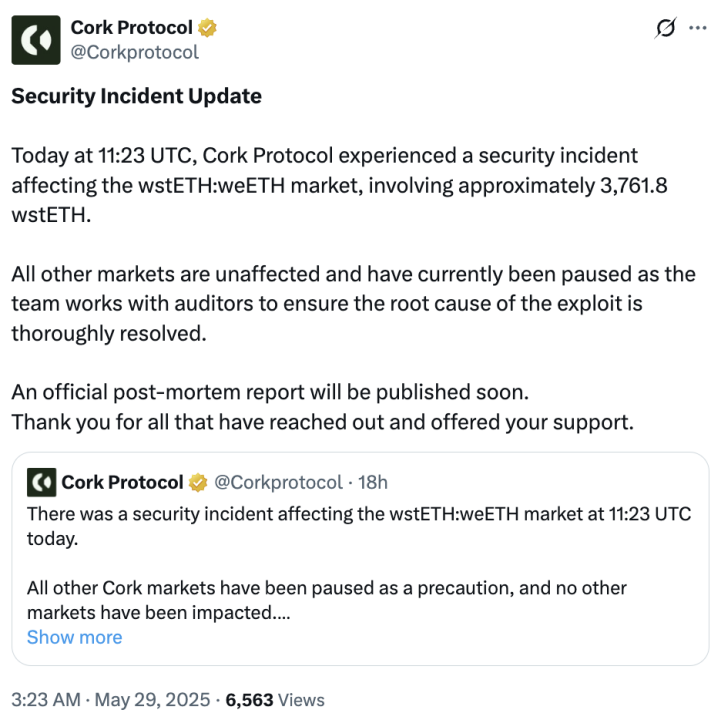
(https://x.com/Corkprotocol/status/1927808041984086083)
After the incident occurred, the SlowMist security team intervened in the analysis immediately. The following is a detailed analysis of the attack methods and fund transfer paths.
Prerequisites
Cork Protocol is a tool designed to provide DeFi ecosystem with a function similar to credit default swaps (CDS) in traditional finance - Depeg Swap, which is specifically used to hedge the depegging risk of pegged assets such as stablecoins, liquidity pledge tokens, RWA, etc. Its core mechanism revolves around the depegging risk of stablecoins and liquidity pledge tokens, allowing users to transfer the price volatility risk of stablecoins or LST/LRT to market participants by trading risk derivatives, thereby reducing risks and improving capital efficiency. The key concepts are as follows:
RA (Redemption Asset): The benchmark asset used in the Cork market to redeem or settle depegging events (e.g. ETH in the ETH::stETH market).
PA (Pegged Asset): An asset with a risk of depegging, which aims to maintain a price peg with RA, but may deviate from the anchor rate due to market volatility, protocol risks, etc. (e.g. stETH in the ETH::stETH market).
DS (Depeg Swap): The core derivative tool issued by the Cork Protocol, used to hedge the risk of depegging. It is essentially similar to the credit default swap (CDS) in traditional finance. Users can purchase such tokens to avoid the risk of depegging.
CT (Cover Token): A derivative instrument paired with DS, used to assume the risk of depegging and earn income, similar to the seller role in CDS. If depegging occurs, the holder will bear the loss.
Exchange Rate: The core parameter for measuring the value relationship between PA and RA, which directly affects the determination of depegging events and the settlement logic of derivative transactions. Currently, the Cork protocol allows users to create markets using custom Exchange Rate Providers.
Cork Vault: Automated management of liquidity across maturities to improve capital efficiency.
Peg Stability Module (PSM): responsible for minting/destroying DS and CT, setting market deadlines, and dynamically adjusting prices through AMM. It allows users to make the following exchanges:
PA + DS = RACT + DS = RA
root cause
The root cause of this attack is that on the one hand, Cork allows users to create any asset as a redemption asset (RA) through the CorkConfig contract, allowing attackers to use DS as RA. On the other hand, any user can call the beforeSwap function of the CorkHook contract without authorization, and allows users to pass in custom hook data for CorkCall operations, allowing attackers to manipulate and deposit DS in the legal market into another market for use as RA, and obtain the corresponding DS and CT tokens.
Attack Analysis
The attacker first purchased weETH8CT-2 tokens on the legitimate market with wstETH so that they could eventually redeem wstETH tokens as RA in combination with DS tokens.
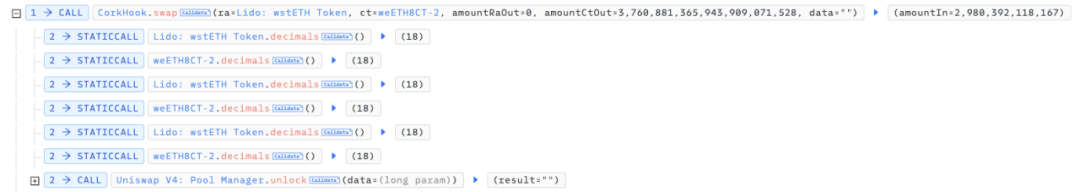
The attacker then created a new market and used a custom Exchange Rate provider. This market was created with weETH8DS-2 tokens as RA and wstETH as PA. Therefore, the key tokens of the new market correspond to the following:
RA: weETH8DS-2PA: wstETHCT: wstETH5CT-3DS: wstETH5DS-3
The key tokens in the market where weETH8DS-2 is located are as follows:
RA: wstETHPA: weETHCT: weETH8CT-2DS: weETH8DS-2
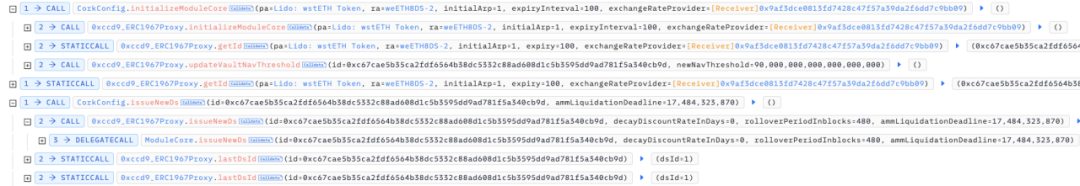
After creating the new market, the attacker adds a certain amount of liquidity to the market so that the protocol can initialize the corresponding liquidity pool in Uniswap v4 so that CorkHook can subsequently execute beforeSwap in this pool.

Next, the most critical thing is that as long as the Uniswap V4 Pool Manager is unlocked, any user can call the beforeSwap function of CorkHook and pass in any parameters to operate the market liquidity of the protocol. Therefore, the attacker uses the unlockCallback function of the Uniswap V4 Pool Manager when it is unlocked to call the beforeSwap function of CorkHook and pass in his customized market and hook data.
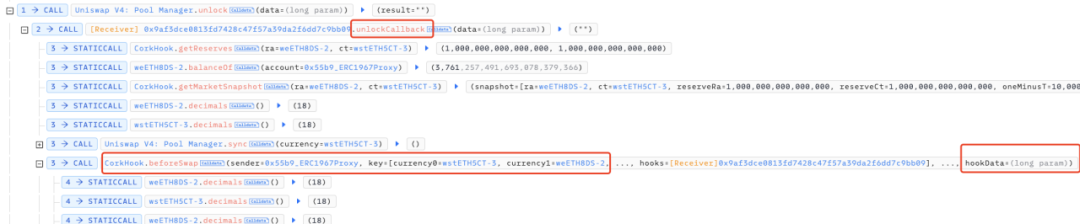
beforeSwap will call back the CorkCall function of the legal market and execute the specified hook data:
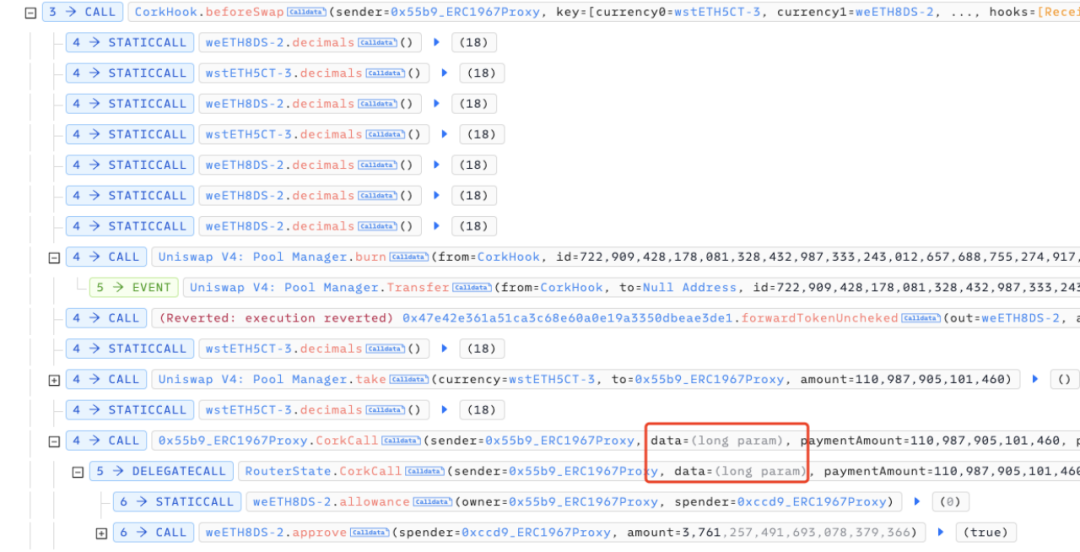
CorkCall trusts the data passed in by the upper-layer legitimate CorkHook and directly parses and executes it:
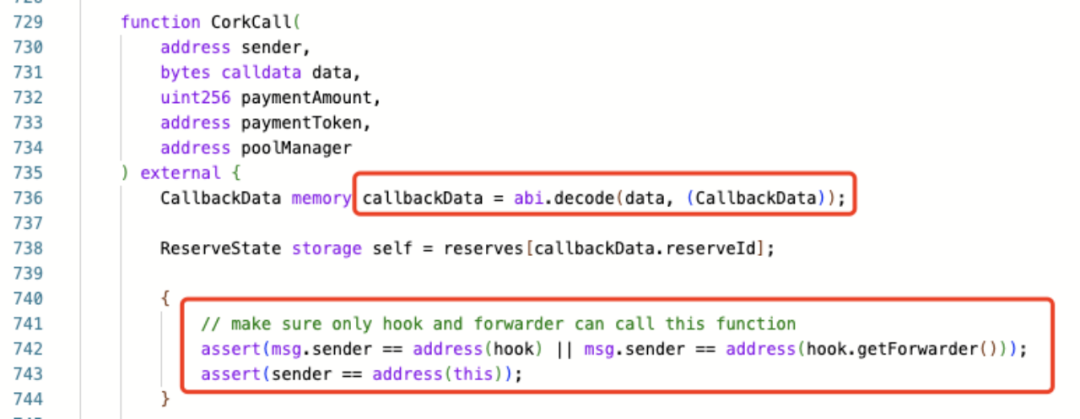
This allows attackers to construct hook data to transfer a specified number of weETH8DS-2 tokens in the legitimate market to the new market they created as RA, and obtain the CT and DS tokens corresponding to the new market.
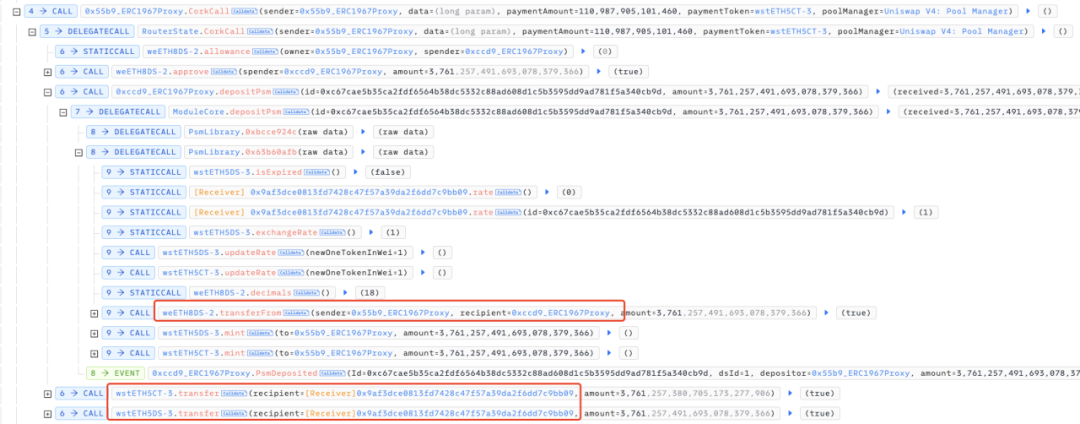
According to the characteristics of PSM, the attacker can use the obtained CT and DS tokens to redeem RA tokens, namely weETH8DS-2 tokens, in the new market.
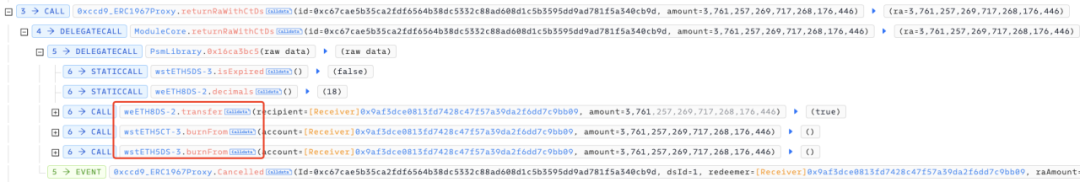
After obtaining the weETH8DS-2 tokens, the attacker can match them with the previously purchased weETH8CT-2 tokens to redeem wstETH tokens in the original market.
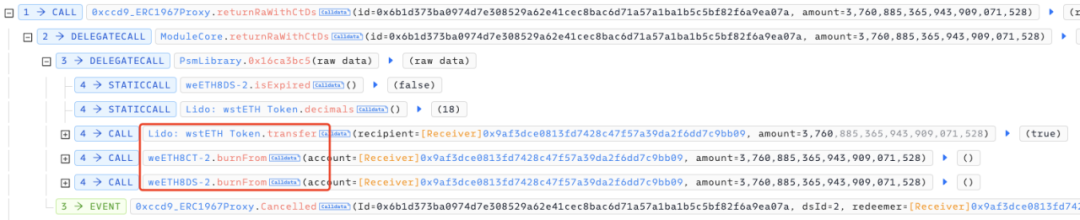
At this point, the attacker took advantage of the fact that the market did not restrict the types of redemption assets and the protocol did not verify the caller and incoming data of CorkHook.beforeSwap, allowing him to transfer the DS liquidity of the legitimate market to another market for redemption as RA, thereby stealing the liquidity of any market.
MistTrack Analysis
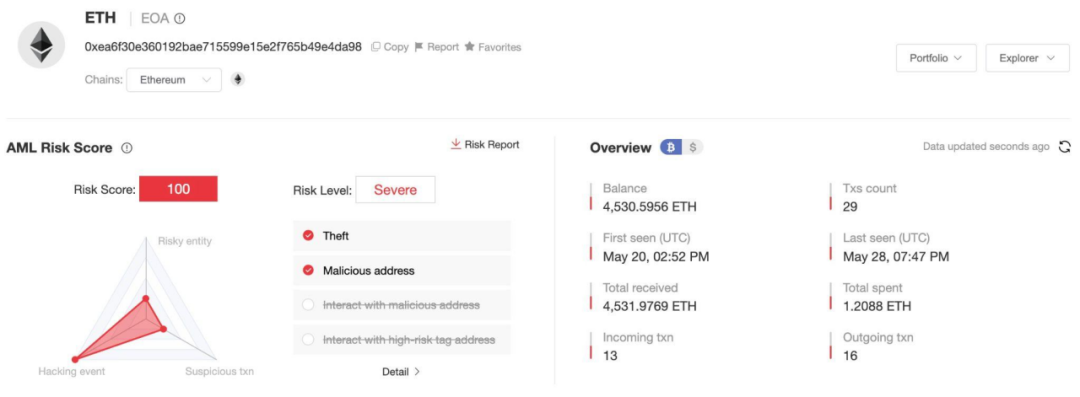
According to the analysis of the on-chain anti-money laundering and tracking tool MistTrack, the attacker's address 0xea6f30e360192bae715599e15e2f765b49e4da98 made a profit of 3,761.878 wstETH, worth more than 12 million US dollars.
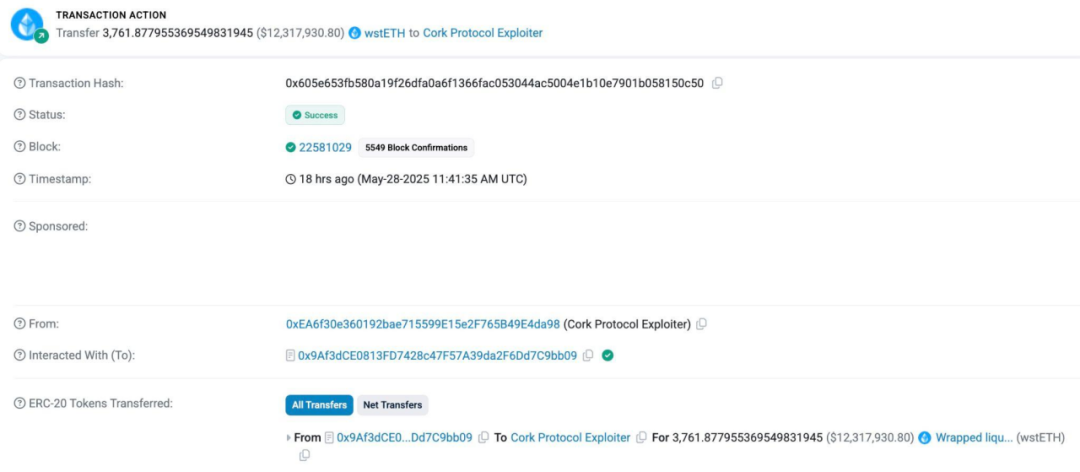
Then, the attacker
8 transactions converted wstETH to 4,527 ETH:
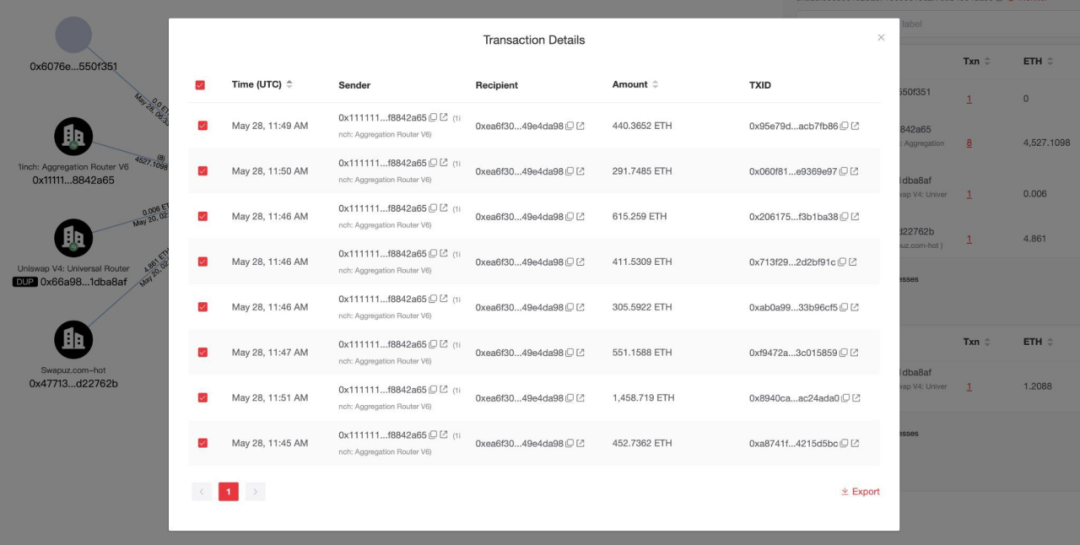
In addition, the attacker’s initial funds came from 4.861 ETH transferred from Swapuz.com.
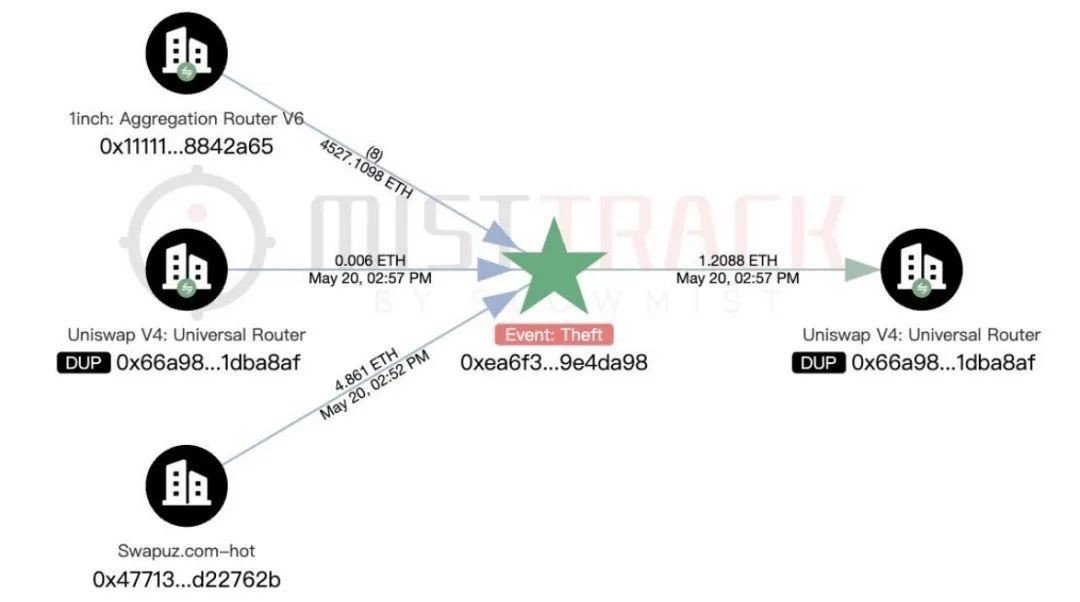
As of now, a total of 4,530.5955 ETH remains in the attacker's address, and we will continue to monitor the funds.
Summarize
The root cause of this attack is that the data passed by users was not strictly verified to be in line with expectations, which allowed the protocol liquidity to be manipulated and transferred to unexpected markets, and then illegally redeemed by attackers for profit. The SlowMist security team recommends that developers should carefully verify whether each step of the protocol is in line with expectations when designing, and strictly limit the types of assets in the market.







